Campus
Drive Questions and Answers
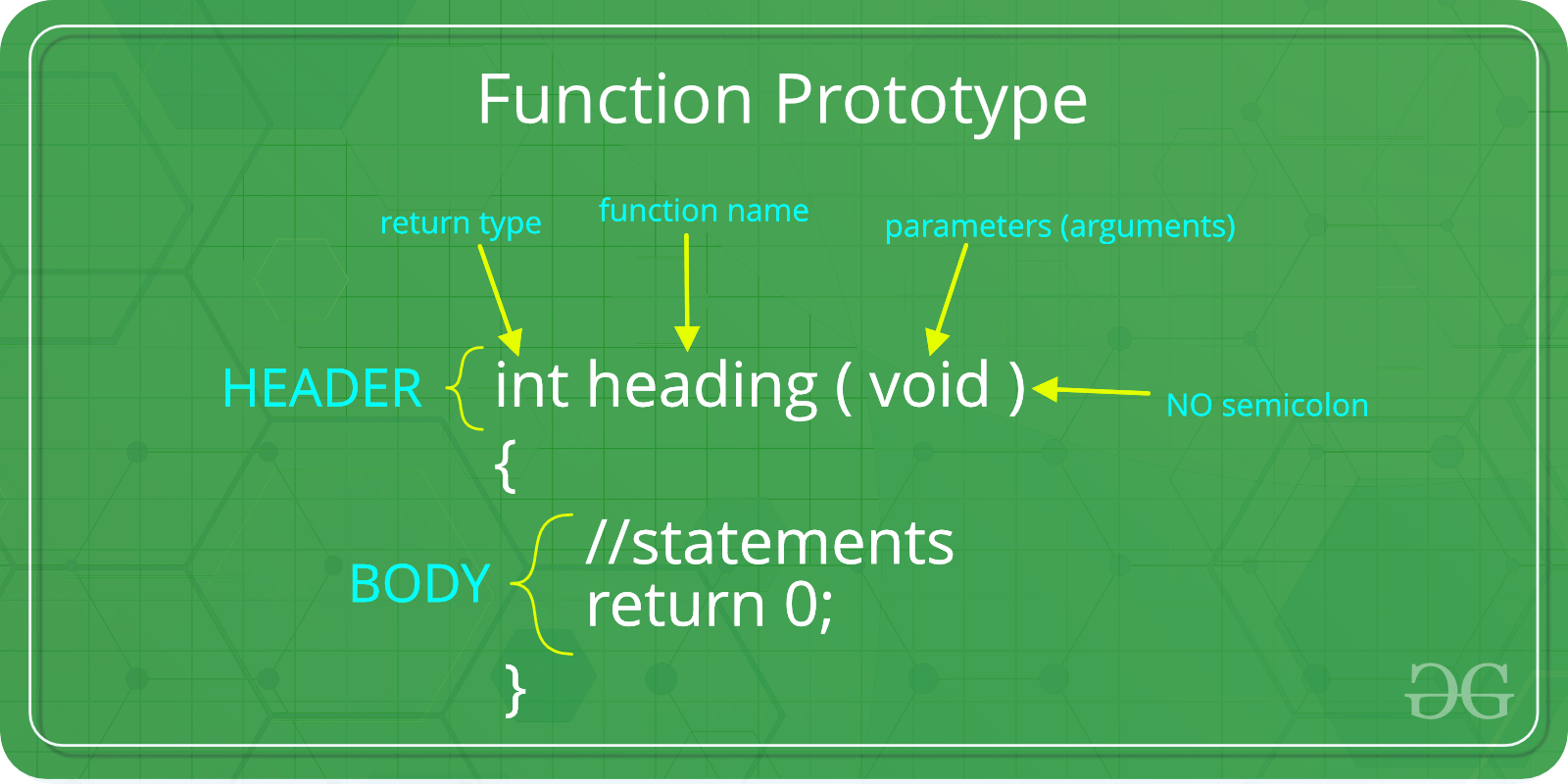
Q) What are main
characteristics of C language?
Ans)
C is a procedural
language. The main features of C language include low-level access to memory,
simple set of keywords, and clean style. These features make it suitable for
system programming like operating system or compiler development.
Q) What is difference between i++ and
++i?
Ans
1) The expression
‘i++’ returns the old value and then increments i. The expression ++i
increments the value and returns new value.
2) Precedence of postfix ++ is higher than that
of prefix ++.
3) Associativity of postfix ++ is left to right
and associativity of prefix ++ is right to left.
4) In C++, ++i can be used as l-value, but i++
cannot be. In C, they both cannot be used as l-value.
Q) What are entry
control and exit control loops?
Ans.
C support only 2 loops:
1. Entry
Control: This loop is categorized in 2 part
a. while loop
b. for loop
2. Exit
control: In this category, there is one type of loop
known as
a. do while loop
Q) Why pre-processor directive does not have a
semi-colon at last?
Ans
Semi-colon
is needed by the compiler and as the name suggests Preprocessors are programs
that process our source code before compilation.Therefore the semi-colon is not required.
Q) What is the difference between including the
header file with-in angular braces < > and double quotes ” “?
Ans
If a header file is included within < >
then the compiler searches for the particular header file only within the
built-in include path. If a header file is included within ” “, then the
compiler searches for the particular header file first in the current working
directory, if not found then in the built-in include path.
Q) How will you print “Hello World” without semicolon?
Ans
Void main()
{
if (printf("Hello World"))
}
Program 1:
#include <stdio.h>
void fun()
{
// static
variables get the default value as 0.
static
int x;
printf("%d
", x);
x
= x + 1;
}
int main()
{
fun();
fun();
return
0;
}
Output: 0 1
Program 2:
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int
i;
int
*pi = &i;
scanf("%d",
pi);
printf("%d\n",
i+5);
}
Output: On execution, the value printed is 5 more than the integer
value entered.
Program 3:
void main()
{
int i=-3,j=2,k=0,m;
m=++i && ++j || ++k;
printf("%d %d %d %d",i,j,k,m);
}
Ans
-2 3 0 1
Program 4:
int f(int j)
{
static int i = 50;
int k;
if (i == j)
{
printf("something");
k
= f(i);
return
0;
}
else return 0;
}
Ans
The function will exhaust the
runtime stack or run into an infinite loop when j = 50
Program 5:
Assume the following C
variable declaration
int *a[10],b[10[10];
Of the following
expressions
i a[2]
ii a[2][3]
iii b[1]
iv b[2][3]
which will give compile-time
errors
Ans:
b[1]
Program 6:
Consider the following declaration of a ‘two-dimensional array in
C:
Char a[100][100];
Assuming that the main memory is byte-addressable
and that the array is stored starting from memory address 0, the address of
a[40][50]
Ans
Address a[i][j] = base address + element size (maximum
number of columns * i + j )
a[40][50]
= 0 + 1 (100 *40 + 50 )
a[40][50]
= 4050
Program 7:
Consider the following declaration of a ‘two-dimensional array in
C:
Char a[10][20][30]; i.e a[M][N][O]
Assuming that the main memory is byte-addressable
and that the array is stored starting from memory address 0, the address of a[4][5][6]
i.e a[i][j][k]
Ans
Address a[i][j][k] = base address + element size (i*N*O
+ j*O + k )
a[4][5][6]
= 0 + 1 (4 * 20 * 30 + 5 * 30 + 6 )
a[4][5][6]
= 2400 + 150 + 6
a[4][5][6]
= 2556
Program 8:
What will be the output of the following C
program segment?
char inchar = 'A';
switch (inchar)
{
case 'A' :
printf
("choice A \n") ;
case 'B' :
printf
("choice B ") ;
case 'C' :
case 'D' :
case 'E' :
default:
printf
("No Choice") ;
}
Ans:
choice A
choice B No Choice
Program 9:
What will be the output of the following C
program segment?
char p[20];
char *s = "string";
int length = strlen(s);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < length; i++)
p[i]
= s[length — i];
printf("%s",p);
Ans
no output is printed
Explanation:
Let us consider below line inside the for loop
p[i] = s[length — i];
For i = 0, p[i] will be s[6 — 0] and s[6] is ‘\0’
So p[0] becomes ‘\0’. It doesn’t matter what comes in p[1], p[2]….. as P[0] will not change for i >0. Nothing is printed if we print a string with first character ‘\0’
p[i] = s[length — i];
For i = 0, p[i] will be s[6 — 0] and s[6] is ‘\0’
So p[0] becomes ‘\0’. It doesn’t matter what comes in p[1], p[2]….. as P[0] will not change for i >0. Nothing is printed if we print a string with first character ‘\0’
Program 10:
Consider the following C program
main()
{
int x,
y, m, n;
scanf ("%d %d", &x, &y);
/* x > 0 and y > 0 */
m = x; n = y;
while (m != n)
{
if(m>n)
m
= m - n;
else
n
= n - m;
}
printf("%d", n);
}
Ans:
GCD (greatest common divisor ) of x and y
Program 11:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
float x=16.3;
if(x==16.3)
printf("HAI");
else
printf("Hello");
}
output :
Program 12:
#include<stdio.h>
#define size 2+4
void main()
{
printf("%d",size*size);
}
output:
Program 13:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i=1;
printf("\n %d\n %d\n %d\n %d",i++,i++,i++,i++);
}
output:
Program 14:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i=5;
printf("\n %d\n %d\n %d\n %d\n %d",i++,i--,++i,--i ,i);
}
output:
Program 15:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6};
printf("%d",1[a]);
}
output:
Program 16:
#include<stdio.h>
int sum (int);
int sum (int n)
{
if(n<1)
return n;
else
return (n + sum(n-1));
}
void main()
{
sum(5);
printf("sum is %d ",sum(5));
}
Answer : 15
Program 17:
#include<stdio.h>
void sum (int ,int ,int );
void sum (int x,int y,int z)
{
y=y+1;
z=z+x;
}
void main()
{
int a=2,b=3;
sum((a+b),a,a);
printf("sum is %d ",a);
}
Answer: 2
Program 17: